Upper Back (Thorasic)
Thorasic Spine Surgeruy
Thoracic spine surgery refers to surgical procedures performed on the thoracic spine, which is the middle portion of the spine located in the upper and mid-back. The thoracic spine consists of 12 vertebrae (T1-T12) and is connected to the ribcage, providing stability and protecting the vital organs in the chest. Surgery in the thoracic spine is less common compared to the cervical (neck) or lumbar (lower back) regions but may be necessary for certain conditions.
Get in touch
Thorasic Spine Surgeruy

Decompression

Instrumented Stabilisation
Decompression

Spinal decompression is a surgical or non-surgical technique aimed at relieving pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots in the spine. The procedure is often employed to address conditions such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or other degenerative changes in the spine causing compression. There are both surgical and non-surgical methods of spinal decompression.
Benefits of Spinal Decompression:
Pain Relief: Decompressing the spine can alleviate pain caused by nerve compression.
Improved Function: Relief from pressure on nerves can result in improved mobility and function.
Prevention of Nerve Damage: Decompression may prevent long-term damage to nerves caused by prolonged compression.
Enhanced Quality of Life: Reduction in pain and improved function contribute to an overall better quality of life for individuals with spinal issues.
Avoidance of Medications: Successful decompression may reduce the need for pain medications used to manage spinal-related symptoms.
It’s important to note that the choice between surgical and non-surgical decompression methods depends on the specific condition, severity, and individual factors. Both approaches aim to alleviate symptoms and improve the overall well-being of individuals with spinal compression issues. The decision should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional based on a thorough evaluation of the patient’s condition.
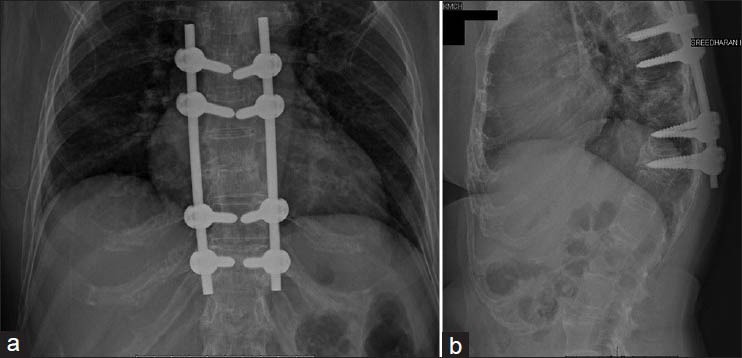
Instrumented Stabilisation
Instrumented spinal stabilization is a surgical procedure that involves the use of hardware or instrumentation to stabilize the spine. This intervention is commonly employed to address conditions such as spinal instability, degenerative disc disease, scoliosis, or fractures. The instrumentation provides support to the spine, promoting proper alignment and preventing excessive movement.
Benefits of Instrumented Spinal Stabilization:
Stabilization: The primary goal is to provide stability to the spine, preventing excessive movement between vertebrae.
Alignment Correction: Instrumentation can help correct abnormal spinal alignment, addressing conditions such as scoliosis.
Pain Relief: Stabilization can alleviate pain associated with spinal instability, fractures, or degenerative conditions.
Facilitation of Fusion: Hardware supports the fusion process by maintaining proper alignment and preventing movement at the fusion site.
Improved Function: Stabilization often leads to improved spinal function and overall mobility.
It’s essential for individuals undergoing instrumented spinal stabilization to discuss potential risks, benefits, and the specific details of the procedure with their healthcare provider. The decision for surgery is typically made based on a thorough evaluation of the patient’s condition and symptoms.

Conclusion
Recovery from thoracic spine surgery varies depending on the specific procedure performed. Patients usually undergo a period of rehabilitation to regain strength, flexibility, and function. As with any surgery, there are potential risks and complications, and individuals considering thoracic spine surgery should discuss these with their healthcare provider to make informed decisions about their treatment.



